[ad_1]
Female Reproductive System: Histology and Organs
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Ovary
- Squamous epithelium = primordial follicle
- Cuboidal epithelium = primary follicle
- Multi-layered cuboidal epithelium = multilaminar primary follicle
- Antrum (fluid-filled space) in the follicle = secondary follicle
- Pink band around the oocyte = zona pellucida
- Theca cells sit outside of the basement membrane of the follicle
- Corpus albicans = dissolving corpus luteum
- Granulosa cells around the ovum in a maturing follicle = corona radiata
- “Stalk” = cumulus oophorus
- Dark pink, rubber-band-like structure inside = atretic follicle
![Medical Anatomy and Histology of Male vs Female Reproductive Organs [Biology, MCAT, USMLE] – Moosmosis Medical Anatomy and Histology of Male vs Female Reproductive Organs [Biology, MCAT, USMLE] – Moosmosis](https://moosmosis.files.wordpress.com/2022/03/image-5.png?w=194)
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Corpus Luteum
- Granulosa cells are lighter staining
- Darker staining fibroblastic cells are theca lutein cells
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Ovary + Fallopian tube
- Fallopian tube epithelium: tall nuclei close to the lumen (Peg cells) and round nuclei (ciliated cells)
- Ampulla has the most tortuous branching pattern; infundibulum has a smaller lumen w/ less branching; intramural portion is surrounded by some myometrial muscle
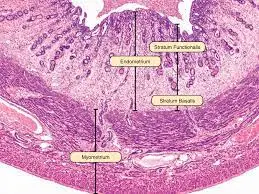
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Uterus
- In tact surface epithelium = not menstrual or immediately post-menstrual
- Endometrium: basalis layer doesn’t change during menstrual cycle – functionalis layer does
- Early proliferative phase: relatively smooth/straight glands in the functionalis +intact surface epithelium
- Secretory phase: coiled glands with secretory product within them in the functionalis + intact surface epithelium + spiral arteries
- Menstrual phase: hemorrhage + functionalis layer sloughing + edema
- Cervix: non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that transitions into simple columnar epithelium with glands
- Vagina: non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with washed-out looking cells (glycogen stored within them)
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Placenta
- Fetal side: large blood vessels and smooth, simple epithelium with two layers of extra-embryonic membranes
- Villi within the placenta
- Round with pale staining cytoplasm = cytotrophoblast
- Continuous and dark staining cytoplasm = syncytiotrophoblast
- Appearance depends on age (younger = more equal representation of cyto- and syncytiotrophoblast)
- Fetal blood is within the villus; maternal blood is in the spaces around the villus
- Macrophages w/in villi = Hofbauer cells
- Decidua/decidual plate = maternal side = modified endometrium
- A large villus that goes all the way across = stem/anchoring villus
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Mammary Gland
- Inactive mammary gland: “islands” of ductal tissue + dense irregular CT
- Proliferative mammary gland: more glandular tissue than CT, development of secretory acini (little circles of cells), lumens haven’t gotten very large
- Lactating mammary gland: dilated acini lumens w/ secretory product inside, more acini than ducts
Male Reproductive System: Organs and Histology
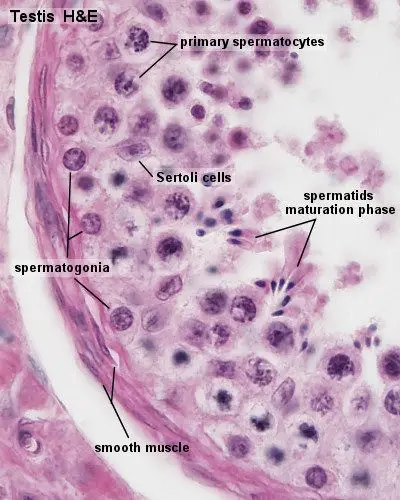
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Testes
- Seminiferous tubule
- Pale staining nucleus + prominent nucleolus = Sertoli Cell
- Small cells with dark nuclei on the BM = spermatogonia
- Cells with condensed chromatin/mitotic figures = primary spermatocytes
- Cells with a very round, condensed nucleus closer to the lumen = early spermatids
- Cells will longer nuclei, starting to take on the appearance of sperm = late spermatids
- Cells between the seminiferous tubules that produce testosterone = Leydig cells
- Dense CT on the surface of the testis = tunica albuginea
- Seminiferous tubule
- Efferent ductules: scalloped glands w/ alternating tall and short cells (have cilia – hard to see)
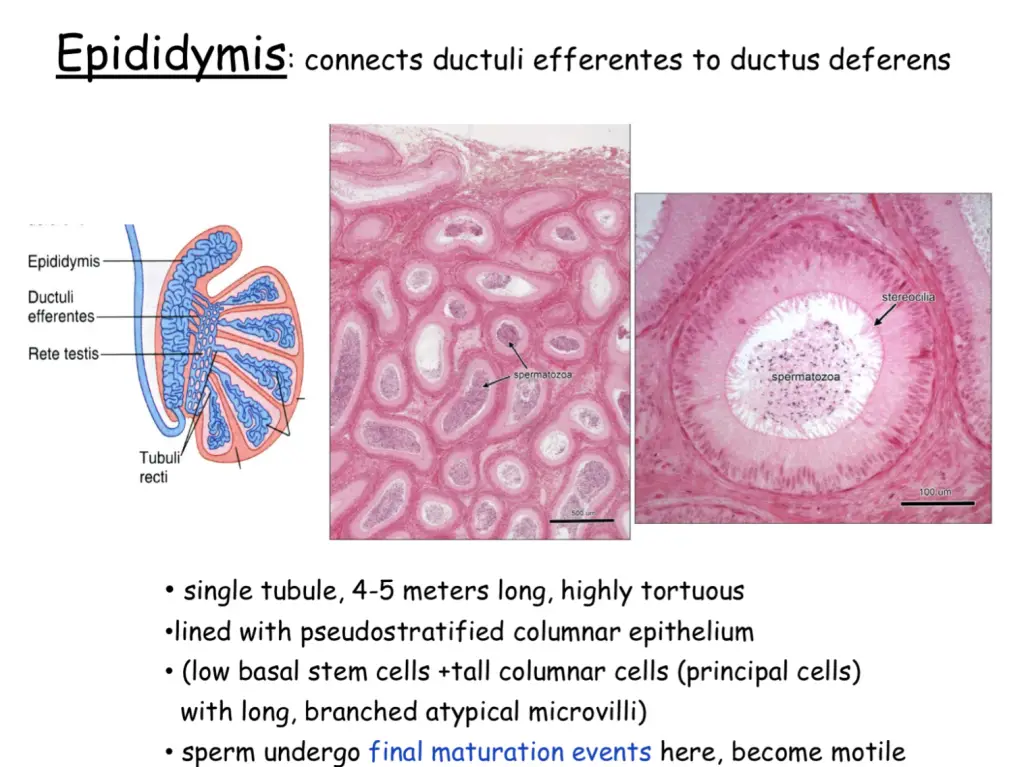
- Epididymis: smooth ductules, stereocilia, pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Mature sperm stored here – only goes to vas deferens pre-ejaculation.
- Note the sperm that arrives at the epididymis is non-motile; the activation (capacitation) occurs here
- Function of stereocilia is absorption of fluid that comes from the testes (to keep things moving along) – this concentrates the sperm
- Vas deferens: large smooth muscle wall (three layers), lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium, basal cells, muscular wall much thicker than the diameter of the lumen
- Urethra: scalloped lumen with muscular wall (only 1-2x the thickness of the lumen), transitional epithelium (binucleate surface cells and multiplelayers)
- Seminal vesicle: convoluted lumen with mucosal crypts, seminal fluid in the lumen, pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Prostate gland: prostatic concretions (laid down in layers, like tree rings), fibromuscular stroma
- Don’t confuse with lactating mammary gland – the CT is very different
- Note: older prostate has more concretions
- Medical Anatomy and Histology: Penis
- Tunica albuginea: CT around the corpora cavernosa
- Corpus spongiosum: penile urethra w/in
Click and check out these popular articles for more information: 🙂
Ectoderm vs Endoderm vs Mesoderm
Psychology 101 and the Brain: Stress – Definition, Symptoms, and Health Effects of the Fight-or-Flight Response
Circulatory System: Blood Flow Pathway Through the Heart
Circulatory System: Heart Structures and Functions
Ductus Arteriosus Vs Ductus Venosus Vs Foramen Ovale: Fetal Heart Circulation
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Upper Vs Lower Respiratory System: Upper vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Seven General Functions of the Respiratory System
Digestive System Anatomy: Diagram, Organs, Structures, and Functions
Kidney Embryology & Development: Easy Lesson
Psychology 101: Crowd Psychology and The Theory of Gustave Le Bon
Introduction to Evolution: Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace

Thank you for visiting, and we hope you find our free content helpful! Our site is run 100% by volunteers from around the world. Please help support us by buying us a warm cup of coffee! Many thanks to the kind and generous supporters and donors for doing so! 🙂
Copyright © 2022 Moosmosis Organization: All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved. This essay or any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever
without the express written permission of the publisher.

[ad_2]
Source link



/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/62810996/Amm_DeepSentinel_01.0.jpg)

More Stories
Benefits and Pros vs Cons – Moosmosis
Steve Hargadon: New Dr. Albrecht Library 2.0 Podcast: “DEI and BELONGING”
Spark Student Creativity with Handmade Gifts